2022年10月17日,北京师范大学认知神经科学与学习国家重点实验室宋艳教授课题组与北京大学第六医院孙黎研究员课题组合作在《Human Brain Mapping》杂志上在线发表题为“Information-based multivariate decoding reveals imprecise neural encoding in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder during visual selective attention”的研究论文。该工作采集了70名注意缺陷多动障碍(ADHD)儿童和65名正常发育儿童进行视觉搜索任务时的脑电和行为数据,通过使用个体化的多变量机器学习的方法,揭示了ADHD儿童目标定向受损与杂乱的神经编码和不精确的位置表征有关(图1)。我们的研究为ADHD儿童的早期诊断和优化个性化干预治疗提供了潜在的研究方向。
注意缺陷多动障碍(ADHD)是一种常见的神经发育性疾病,大约5%的学龄期儿童存在ADHD,这直接影响了许多高级认知功能和学习成绩。然而,ADHD儿童的潜在病理生理学基础仍不清楚。我们仍然缺乏临床生物标志物来帮助对ADHD儿童进行早期诊断和干预。

图1. 杂乱神经编码假说和多变量机器学习方法在ADHD认知脑电上的运用
本研究首次将多变量机器学习的方法用在ADHD儿童的临床认知研究中,结果发现ADHD儿童对于目标位置的神经解码准确率显著低于且慢于正常发育儿童(图2),且与注意选择相关的ERP成分N2pc不存在相关性,这表明 ADHD 儿童使用与正常发育儿童不同的潜在神经机制来处理空间定位。 这可能是构成ADHD 儿童临床生物标志物的基础,这种杂乱的神经编码推动了我们对神经发育性障碍的认知损伤的理解。此外,使用多变量机器学习的方法在ADHD儿童认知脑电中的运用架起了基础研究转化到临床转化的桥梁。
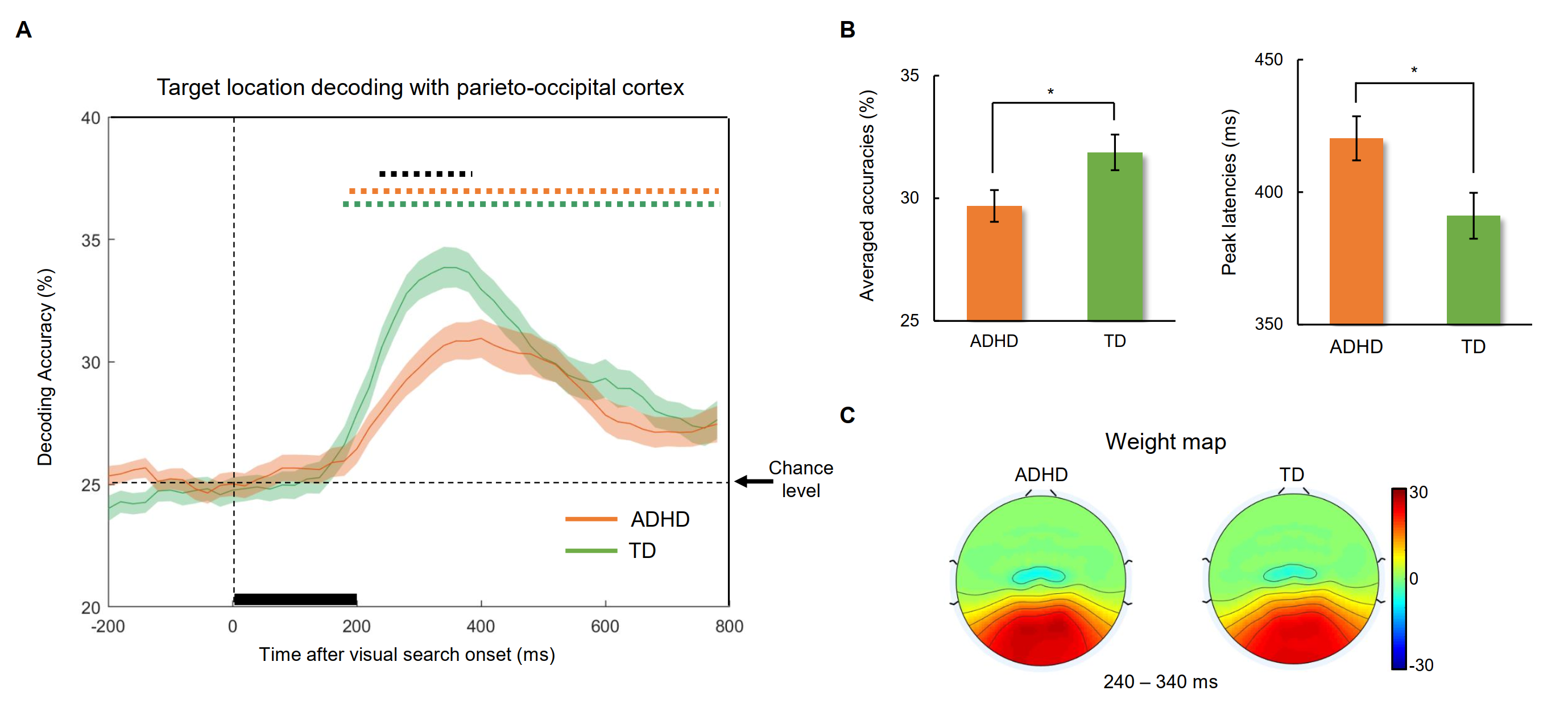
图2. 目标位置的神经解码准确率和权重分布。ADHD儿童表现出较低且延迟的神经解码精度。
该项研究工作得到了国家自然科学基金(31871099,81971284, 81771479),北京市科委(Z171100001017089)等项目的资助。论文第一作者为北师大宋艳课题组博士生李东伟,北大六院孙黎课题组罗翔升博士(现为安定医院临床医生)为论文的并列第一作者,通讯作者为北京师范大学宋艳教授和北京大学第六医院孙黎研究员;宋艳课题组成员博士后郭家梁,博士生孔元君,硕士生胡怡清,北京大学第六医院王玉凤教授, 孙黎课题组硕士生陈严博和祝雨,也对此项工作做出了重要贡献。
文章链接:
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/hbm.26115
宋艳课题组关于ADHD儿童脑电的系列研究成果:
1. Guo, J., Luo, X., Kong, Y., Li, B., Si, B., Sun, L., & Song, Y. (2022). Abnormal Reactivity of Brain Oscillations to Visual Search Target in Children With Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging.
2. Li, B., Guo, J., Zhao, C., Luo, X., Kong, Y., Chen, Y., ... & Song, Y. (2022). Lack of an association between anticipatory alpha oscillations and attentional selection in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Clinical Neurophysiology, 138, 25-37.
3. Luo, X., Guo, J., Li, D., Liu, L., Chen, Y., Zhu, Y., ... Song Y & Sun, L. (2021). Atypical Developmental Trajectories of Early Perception Among School-Age Children With Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder During a Visual Search Task. Child Development, 92(6), e1186-e1197.
4. Guo, J., Luo, X., Li, B., Chang, Q., Sun, L., & Song, Y. (2020). Abnormal modulation of theta oscillations in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. NeuroImage: Clinical, 27, 102314.
5. Guo, J., Luo, X., Wang, E., Li, B., Chang, Q., Sun, L., & Song, Y. (2019). Abnormal alpha modulation in response to human eye gaze predicts inattention severity in children with ADHD. Developmental cognitive neuroscience, 38, 100671.
6. Luo, X., Guo, J., Liu, L., Zhao, X., Li, D., Li, H., ...Song Y & Sun, L. (2019). The neural correlations of spatial attention and working memory deficits in adults with ADHD. NeuroImage: Clinical, 22, 101728.
7. Sun, M., Wang, E., Huang, J., Zhao, C., Guo, J…& Song, Y. (2018). Attentional selection and suppression in children and adults. Developmental Science, e12684.